责任链模式
责任链模式:也叫职责链模式。是一种行为型设计模式,它将请求的发送者和接收者解耦,使多个对象都有机会处理请求。请求沿着一个链传递,直到有一个对象能够处理它为止。
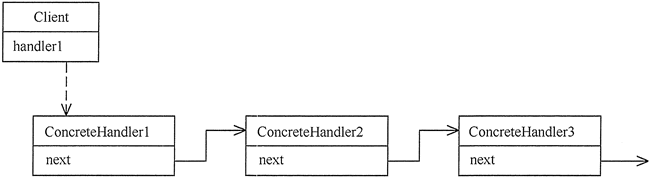
在责任链模式中,通常会有一个抽象处理者(Handler)作为链条的基础,每个具体处理者(ConcreteHandler)都继承自抽象处理者,并且持有下一个处理者的引用。当一个请求到达时,它会首先被发送给链条的第一个处理者,如果该处理者能够处理请求,就处理它;否则,它会将请求传递给下一个处理者,直到有一个处理者能够处理请求或者请求到达链条的末尾。
用图表示如下:
 责任链模式的优点:
责任链模式的优点:
解耦请求发送者和接收者:请求发送者不需要知道具体的接收者,而是将请求发送给链条的第一个处理者,由处理者自行决定是否能够处理请求。
可扩展性:可以灵活地增加、修改或重新排列处理者,以满足不同的需求,而无需修改客户端代码。
动态组合:可以动态地组合处理者,根据实际情况灵活地创建责任链。
责任链模式的缺点:
请求可能无法被处理:如果没有处理者能够处理请求,那么请求可能会到达链条的末尾而无法得到处理。
性能考虑:由于请求需要在链条中传递,如果链条过长或者处理者的处理逻辑复杂,可能会影响性能。
可能导致系统难以调试:由于请求的处理过程是动态的,可能会导致难以跟踪和调试问题。
责任链模式的主要角色如下。
抽象处理者(Handler)角色:定义一个处理请求的接口,包含抽象处理方法和一个后继连接。
具体处理者(Concrete Handler)角色:实现抽象处理者的处理方法,判断能否处理本次请求,如果可以处理请求则处理,否则将该请求转给它的后继者。
客户类(Client)角色:创建处理链,并向链头的具体处理者对象提交请求,它不关心处理细节和请求的传递过程。
责任链模式的实现
// 抽象处理者角色
abstract class Handler {
private Handler next;
public void setNext(Handler next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Handler getNext() {
return next;
}
//处理请求的方法
public abstract void handleRequest(String request);
}
// 具体处理者角色1
class ConcreteHandler1 extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("one")) {
System.out.println("具体处理者1负责处理该请求!");
} else {
if (getNext() != null) {
getNext().handleRequest(request);
} else {
System.out.println("没有人处理该请求!");
}
}
}
}
// 具体处理者角色2
class ConcreteHandler2 extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("two")) {
System.out.println("具体处理者2负责处理该请求!");
} else {
if (getNext() != null) {
getNext().handleRequest(request);
} else {
System.out.println("没有人处理该请求!");
}
}
}
}
// 测试类
public class ChainOfResponsibilityTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//组装责任链
Handler handler1 = new ConcreteHandler1();
Handler handler2 = new ConcreteHandler2();
handler1.setNext(handler2);
//提交请求
handler1.handleRequest("two");
}
}程序运行结果如下:
具体处理者2负责处理该请求!责任链模式在Mybatis中的应用
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(
MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject,
BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement
.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement,
parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor,
MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds,
ParameterHandler parameterHandler, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(
executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler,
boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor,
MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(
executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction,
ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ?
defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ?
ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
} 插件是用来包装四大对象,拦截指定的方法:
Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
package org.apache.ibatis.plugin;
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
private final Interceptor interceptor;
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>,
Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(
interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method,
args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
}责任链模式在Spring Aop中的应用
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {
/** The configuration used to configure this proxy. */
protected final AdvisedSupport advised;
public CglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");
if (config.getAdvisorCount() == 0 && config.getTargetSource()
== AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {
throw new AopConfigException("...");
}
this.advised = config;
this.advisedDispatcher = new AdvisedDispatcher(this.advised);
}
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
……
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
……
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
aopInterceptor,
targetInterceptor,
new SerializableNoOp(),
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
……
}
else {
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args,
MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the
// target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ?
target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised
.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method,
targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the
// target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(
method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke
// the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an
// InvokerInterceptor, so we know it does nothing but a
// reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping
// or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils
.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method,
args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
}
private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation {
@Nullable
private final MethodProxy methodProxy;
public CglibMethodInvocation(Object proxy,
@Nullable Object target,
Method method, Object[] arguments,
@Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers,
MethodProxy methodProxy) {
super(proxy, target, method, arguments, targetClass,
interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers);
// Only use method proxy for public methods not derived from
// java.lang.Object
this.methodProxy = (Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()) &&
method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class &&
!AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method) &&
!AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method) &&
!AopUtils.isToStringMethod(method) ?
methodProxy : null);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
try {
return super.proceed();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(),
ex.getClass())) {
throw ex;
}
else {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex);
}
}
}
/**
* Gives a marginal performance improvement versus using
* reflection to invoke the target when invoking public methods.
*/
@Override
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
if (this.methodProxy != null) {
return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments);
}
else {
return super.invokeJoinpoint();
}
}
}
}
public class AdvisedSupport extends ProxyConfig implements Advised {
AdvisorChainFactory advisorChainFactory =
new DefaultAdvisorChainFactory();
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached == null) {
cached = this.advisorChainFactory
.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
}
public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions
// first, but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry
.getInstance();
Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors();
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(advisors.length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ?
targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
Boolean hasIntroductions = null;
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut()
.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut()
.getMethodMatcher();
boolean match;
if (mm instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
if (hasIntroductions == null) {
hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(
advisors, actualClass);
}
match = ((IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) mm)
.matches(method, actualClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
match = mm.matches(method, actualClass);
}
if (match) {
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry
.getInterceptors(advisor);
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the
// getInterceptors() method isn't a problem
// as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
interceptorList.add(
new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(
interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(
actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(
advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(
advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}
}
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex ==
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(
++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will
// already have been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher)
interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ?
this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass,
this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut
// will have been evaluated statically before this object
// was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice)
.invoke(this);
}
}
} @Before、@After、@Around注解分别对应AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice、AspectJAfterAdvice、AspectJAroundAdvice这三个增强器。
package org.springframework.aop.aspectj;
public class AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice, Serializable {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args,
@Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return false;
}
}
public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
}
public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean supportsProceedingJoinPoint() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("......");
}
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
protected ProceedingJoinPoint lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(
ProxyMethodInvocation rmi) {
return new MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint(rmi);
}
}
public class AspectJAfterReturningAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setReturningName(String name) {
setReturningNameNoCheck(name);
}
@Override
public void afterReturning(@Nullable Object returnValue, Method method,
Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
if (shouldInvokeOnReturnValueOf(method, returnValue)) {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), returnValue, null);
}
}
private boolean shouldInvokeOnReturnValueOf(Method method,
@Nullable Object returnValue) {
Class<?> type = getDiscoveredReturningType();
Type genericType = getDiscoveredReturningGenericType();
// If we aren't dealing with a raw type, check if generic
// parameters are assignable.
return (matchesReturnValue(type, method, returnValue) &&
(genericType == null || genericType == type ||
TypeUtils.isAssignable(genericType,
method.getGenericReturnType())));
}
private boolean matchesReturnValue(Class<?> type, Method method,
@Nullable Object returnValue) {
if (returnValue != null) {
return ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, returnValue);
}
else if (Object.class == type && void.class == method
.getReturnType()) {
return true;
}
else {
return ClassUtils.isAssignable(type, method.getReturnType());
}
}
}
public class AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setThrowingName(String name) {
setThrowingNameNoCheck(name);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
private boolean shouldInvokeOnThrowing(Throwable ex) {
return getDiscoveredThrowingType().isAssignableFrom(ex.getClass());
}
}